Table of Contents
Python + Filters + FFT + Gnuplot
Noise
Filters
Linear filters
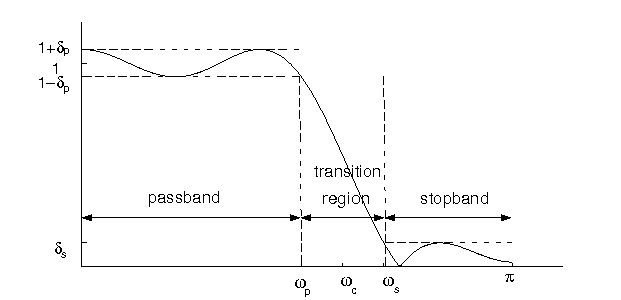
There are five basic parameters to design a filter: wp (pass frequency), ws (stop frequency), gpass (pass gain), gstop (stop gain), filter type
Non linear filters
Median filter
Sharpness: high pass filter
Fast Fourier Transform
Example
The following example code takes data from a phidget analog input and filters this signal using first a IIR filter, then a median and then it calculates the FFT of the whole signal.
import scipy.signal as filters
class filter:
def __init__(self,wp,ws,gpass,gstop):
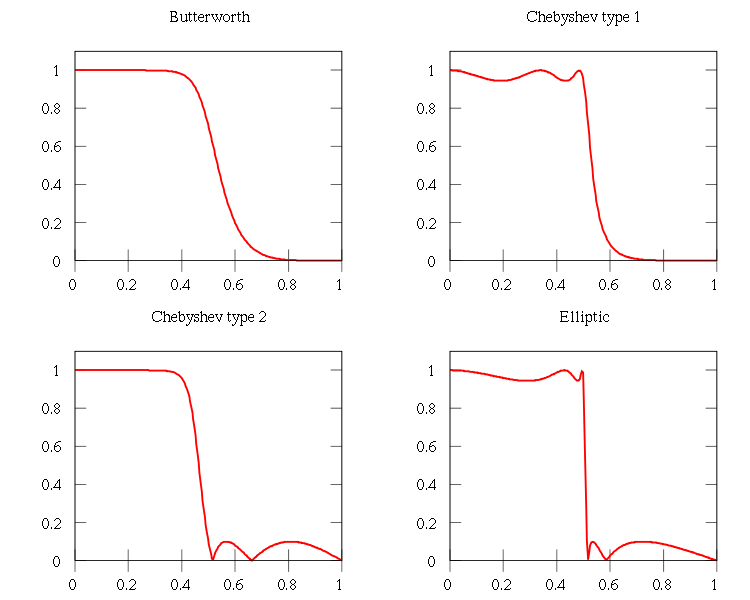
self.b,self.a=filters.iirdesign(wp,ws,gpass,gstop,ftype='ellip')
self.z=filters.lfiltic(self.b,self.a,[])
self.M=len(self.b)-1
self.N=len(self.a)-1
self.K=max(self.M,self.N)
def get_output(self,input):
'''input must be of size N'''
self.output,self.z=filters.lfilter(self.b,self.a,input,zi=self.z)
return(self.output)
def get_N(self):
return self.N
def get_ab(self):
return([self.a,self.b])
N=property(get_N)
from Phidgets.PhidgetException import *
from Phidgets.Events.Events import *
from Phidgets.Devices import *
import numpy as n
ik=InterfaceKit.InterfaceKit()
ik.openPhidget()
ik.waitForAttach(10000)
my_filter=filter(0.1,0.3,1,60)
N=my_filter.N
time_array=[]
total_input=[]
total_output=[]
import time
inittime=time.time()
while True:
t=[]
input=[]
for i in range(N):
t.append(time.time()-inittime)
input.append(ik.getSensorValue(0))
time.sleep(0.05)
output=my_filter.get_output(input)
time_array=n.concatenate((time_array,t))
total_input=n.concatenate((total_input,input))
total_output=n.concatenate((total_output,output))
if t[-1]>10:
break
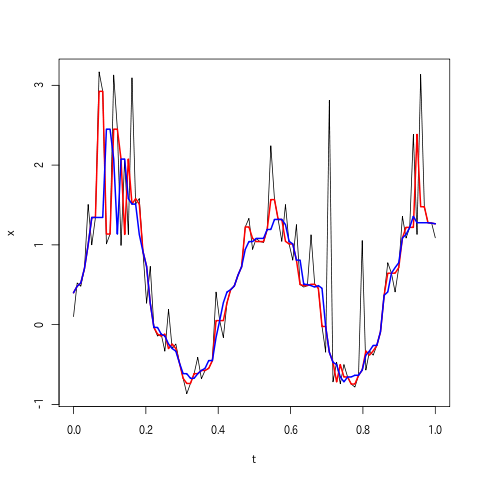
total_output_median=filters.medfilt(total_input,kernel_size=11)
import Gnuplot
g=Gnuplot.Gnuplot()
g.title("filter")
g('set data style linespoints')
g.plot(zip(time_array,total_input),zip(time_array,total_output))
raw_input()
import scipy
from math import pi
fft=scipy.fft(total_input)
g.plot(zip(n.arange(0,pi,pi/len(fft)),fft[0:len(fft)/2]))
raw_input()
g.plot(zip(time_array,total_input),zip(time_array,total_output_median))
a,b=my_filter.get_ab()
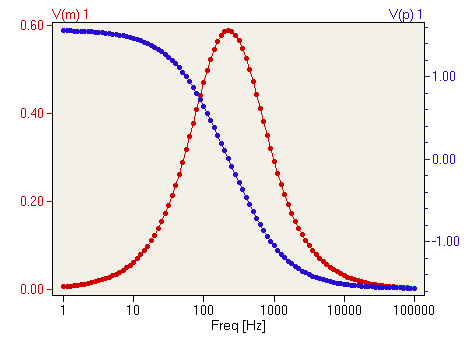
w,h=filters.freqz(b,a)
from numpy import log10
h_db=20*log10(abs(h))
raw_input()
g.plot(zip(w/max(w),h_db))
while True:
time.sleep(0.1)
fastdev/python_signals.txt · Last modified: by memeruiz · [Old revisions]